





 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Topics >> by >> the_of_software_engineering |
| the_of_software_engineering Photos Topic maintained by (see all topics) |
||
The Ultimate Guide To Prototyping Model in Software Engineering - worldofitechWhat is Prototyping Model? is a software application advancement design in which model is built, checked, and revamped till an acceptable prototype is accomplished. It likewise creates base to produce the last system or software application. It works best in circumstances where the task's requirements are not understood in information. It is an iterative, experimentation approach which takes place in between developer and customer. 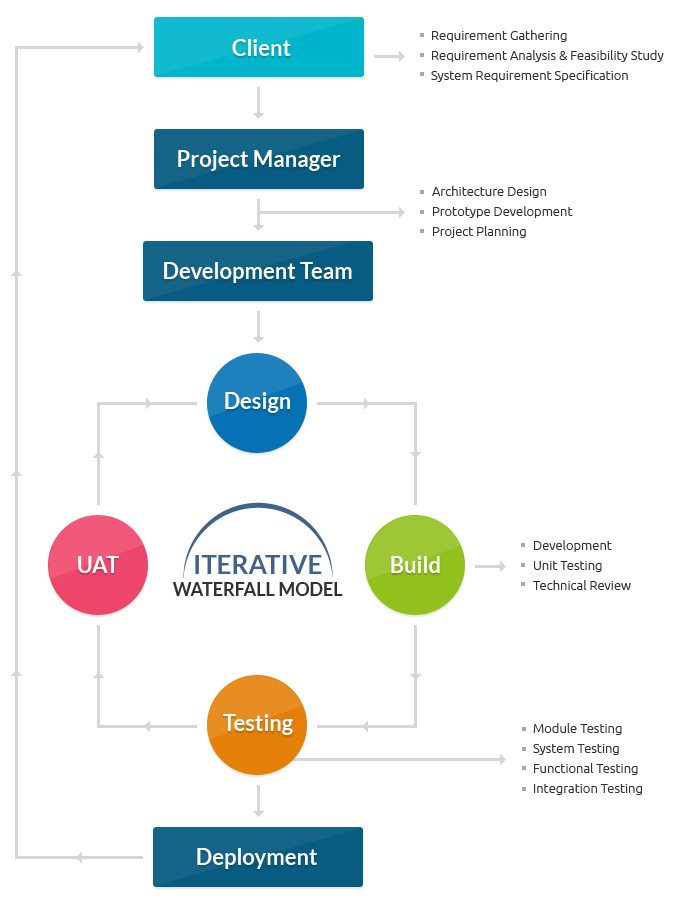 In this stage, the requirements of the system are defined in detail. During I Found This Interesting , the users of the system are interviewed to understand what is their expectation from the system. Action 2: Quick style The second stage is an initial design or a quick style. In this stage, a basic style of the system is created.  It provides a quick concept of the system to the user. The quick design helps in developing the model. Step 3: Build a Model In this stage, a real model is designed based upon the information gathered from fast design. It is a small working model of the necessary system. Some Of What is the difference between Build fix model and prototypeIt helps to discover the strength and weak point of the working model. Comment and suggestion are gathered from the client and provided to the designer. Step 5: Refining prototype If the user is not pleased with the existing prototype, you need to fine-tune the prototype according to the user's feedback and suggestions. Once the user is satisfied with the developed model, a final system is established based on the authorized last model. Action 6: Implement Product and Maintain Once the final system is developed based upon the final prototype, it is thoroughly tested and released to production. The system undergoes routine upkeep for lessening downtime and avoid large-scale failures. It is quickly established to show how the requirement will look visually. The consumer's feedback assists drives modifications to the requirement, and the model is again produced until the requirement is baselined. In this method, a developed model will be disposed of and will not be a part of the eventually accepted model. |
||
|
||