The many body programs undergo several change, and the most are immature at birth. Every should be seen closely pertaining to proper functioning and adjustment to extra-uterine existence.
Fluid and electrolyte harmony
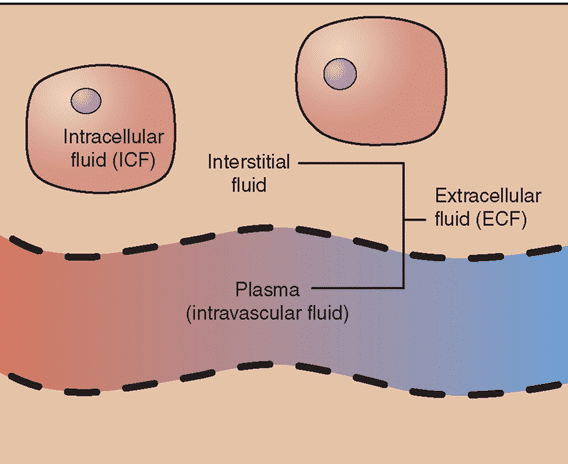
Changes result from the total body water quantity, extra-cellular liquid volume, and intracellular fluid volume through the transition out of fetal to postnatal personal life. The early child is composed nearly entirely of water and at term is certainly 73% solution, as compared to 58% in the individual. There is a a higher level00 extracellular fluid than intracellular fluid inside fetus.
The infant has a proportionately higher relative amount of extracellular fluid than the adult and therefore has a level of00 total body salt and chloride and a reduced level of potassium, magnesium, and phosphate. Besides, the rate of fluid exchange being seven times more significant in the baby in relation to bodyweight. As a result, twice as much acid is formed, resulting to more rapid advancement acidosis. Intracellular Fluid cannot sufficiently concentrate a stream of urine to conserve human body water.
Thermoregulation
The neonate's body temperature regulatory mechanisms are affected by several key elements. At birth, the newborn's capacity for production is certainly adequate nonetheless is dependent in increased metabolic activity. The important task in the thermo-regulation of this neonate can be therefore to minimize the difference among heat generation and temperature loss.
The infant's proportionately larger area in relation to bodyweight provides further exposure to the surroundings and larger heat loss per product of weight. However , resource efficiency of heat is aided by the newborn's usual placement of flexion, which minimizes the surface location exposed to environmental surroundings. Another anatomic factor the fact that retards the conservation of body heat is definitely the newborn's slim layer of subcutanoes unwanted fat. Since main body temperature is approximately 1 levels higher than area body temperature, that temperature lean will cause some heat transfer from an increased to lower temperatures. The major source of body heat from the newborn will be the heart, failing liver, and chemistry of the brain. However , there is an additional resource unique into the neonate that could be referred to as darkish adipose muscle (BAT), or maybe brown weight.
Brown excessive fat, which owes its name to its greater content of mitochondrial cytochromes, has a larger capacity for heat up production because of intensified metabolic activity as opposed to ordinary obésité tissue. High temperature generated inside brown extra fat is sent out to various parts of the physique by the bloodstream, which is heated as it flows through the layers of this tissues. Superficial deposit of dark brown fat are placed between the scapula, around the neck of, and back of the sternum. Deeper coatings surround the Kidneys, trachea, esophagus, a handful of major blood vessels, and adrenals. The location from the brown fat may clarify why the nape with the neck typically feels warmer than the rest of the infant's body.
|











