





 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Topics >> by >> what_does_a_slab_foundation |
| what_does_a_slab_foundation Photos Topic maintained by (see all topics) |
||
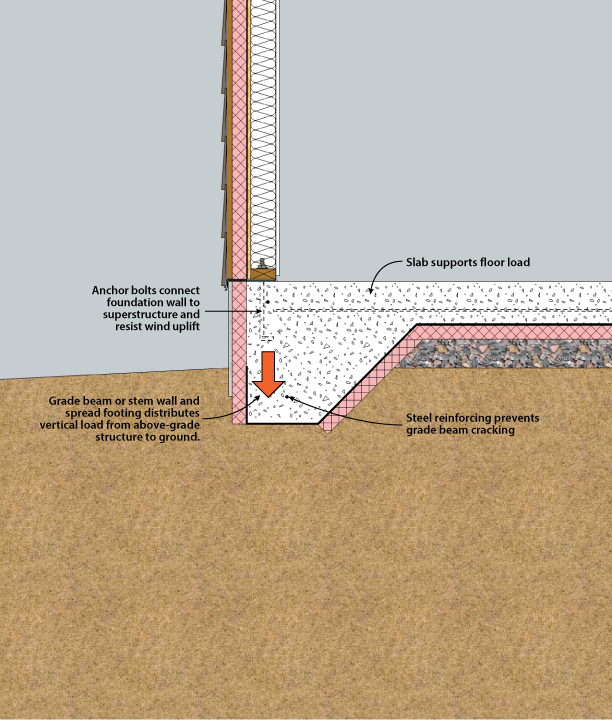 8 Easy Facts About Manufactured Homes: Pier VsSlab Foundation - Hunker ExplainedThe main one is the climate. Especially in the United States, there is a distinction in the popularity of structure types based upon the environment of a region. For instance, in more temperate climates, installing a monolithic piece structure can increase overall energy performance. In desert climates, a crawl space might be best for this purpose, while in freezing climates, it's probably a basement. In a location with a high water table, for instance, slab and crawl area structures are preferabale. The same holds true in areas with sandy soils, such as desert locations, or areas where bedrock is close to the ground surface, such as mountainous areas. A study by the National Association of Home Builders found that 84% of houses in the upper Midwest had basements but less than 1% of homes in Texas, Louisiana, and Oklahoma did. There are lots of variations of concrete pieces depending on the purpose of the piece. Below are some helpful links for understanding concrete foundations, in addition to the 3 kinds of concrete structures. T-Shaped T-Shaped A conventional foundation technique to support a structure in an area where the ground freezes. A footing is placed below the frost line and then the walls are included on top.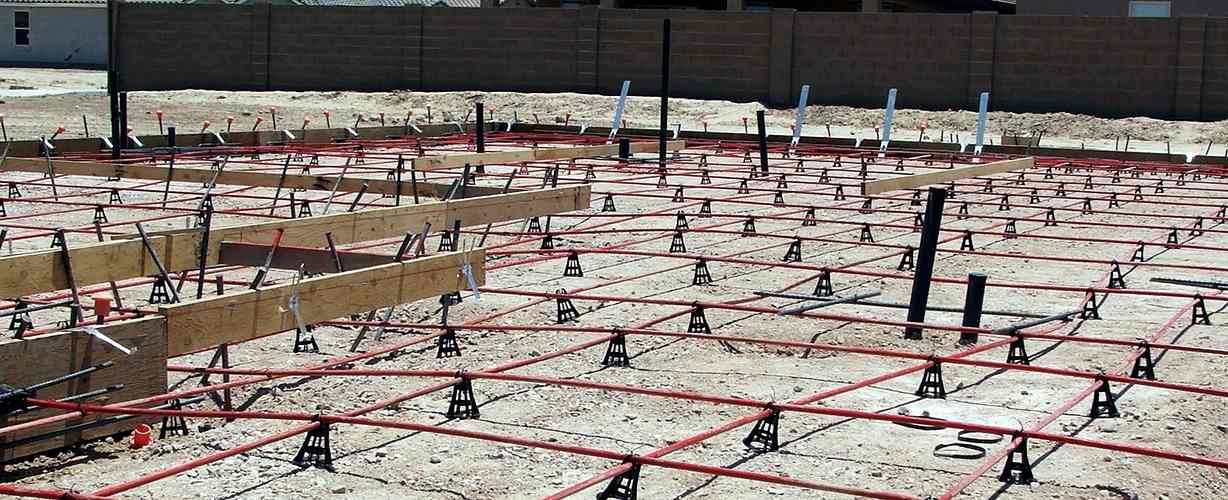  Some Known Details About Create a Foundation Slab - Revit 2019 - Autodesk KnowledgeA T-shaped structure is positioned and permitted to cure; second, the walls are built; and lastly, the piece is poured between the walls. In summary: T-shaped structures are used in areas where the ground freezes. First, the footing is positioned. Second, the walls are constructed and poured. Lastly, the slab is positioned.  The piece is poured thicker at the edges, to form an integral footing; strengthening rods enhance the thickened edge. The piece normally rests on a bed of crushed gravel to enhance drain. Casting Did you see this? in the concrete lowers the possibility of breaking. A piece on grade appropriates in locations where the ground doesn't freeze, but it can also be adjusted with insulation to avoid it from being impacted by the frost heaves.  |
||
|
||