Atoms, molecules, components, isotopes... A BUMMER! Well, it really is for some people, although personally, I believe it's somewhat fascinating. For one thing, everything across the world is made from all these invisible allergens. Although it might seem of atoms when visualizing the smallest "thing" in the world, every time asking yourself what an atom is made of, it becomes clear there is smaller contaminants.
What is an Atom?
Atoms are made out of combining electrons, protons, and neutrons - subatomic particles. Just how many of these some subatomic dust an atom contains will depend on what chemical substance element the idea belongs to. Atoms are categorized by the one of a kind number of protons within their nucleus supports this is the atomic quantity. A stable atom must have an equal number of protons and electrons.
Protons have a very good positive electric power charge even though electrons have a negative 1. Therefore , if there are even more protons than electrons, you have a confidently charged ion, also known as a good cation. Having said that, if you have even more electrons than protons, you may have a negatively charged ion, also known as an anion. Atoms with a net sale electrical charge as referred to can be produced so synthetically from a good neutral status by ionizing radiation.
Therefore we protected protons and electrons, but you may be wondering what does the ungeladenes nukleon do? Good, you can think of neutrons as the stuff that binds the protons together. Why do they have to be locked together? As stated above, protons and electrons will be electrically costed, and as such, will naturally repel particles of the same indication. This is why groups of protons need to have neutrons to maintain them along. Hydrogen-1 does not have any sort of neutrons simply because it only has one proton.
What is a great Isotope?
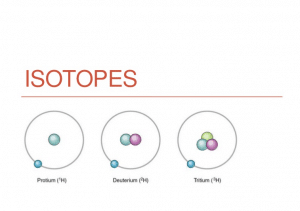
Thus we know that the atomic number is derived from how many protons in the atom's nucleus, but what about isotopes? https://higheducationhere.com/isotopes/ is certainly defined by the number of neutrons in an atom's nucleus. Within a given chemical substance element, there is often a number of these isotopes. For instance , hydrogen offers 1 wasserstoffion (positiv) (fachsprachlich), but determined by what hydrogen isotope it can be, the number of neutrons vary.
Isotopes are called by their provided chemical feature, followed by their particular atomic fast, as in hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, etc. This means that although the number of protons remains frequent, the number of neutrons changes. Therefore hydrogen-2 will have a neutron as well as a proton, while hydrogen-3 will have 2 neutrons and a wasserstoffion (positiv) (fachsprachlich). Hydrogen-1 offers only 1 proton and no neutrons.
By subtracting the atomic number in the mass quantity, you find the number of neutrons. Isotopes might be recognized on paper by a component name and a distinct majority number that include hydrogen-3 as well as iodine-131. Once speaking of various isotopes, radioactive or certainly not, they will be diagnosed by name. Therefore , familiarizing yourself together with the structure from atoms and related words can be helpful.
|











