





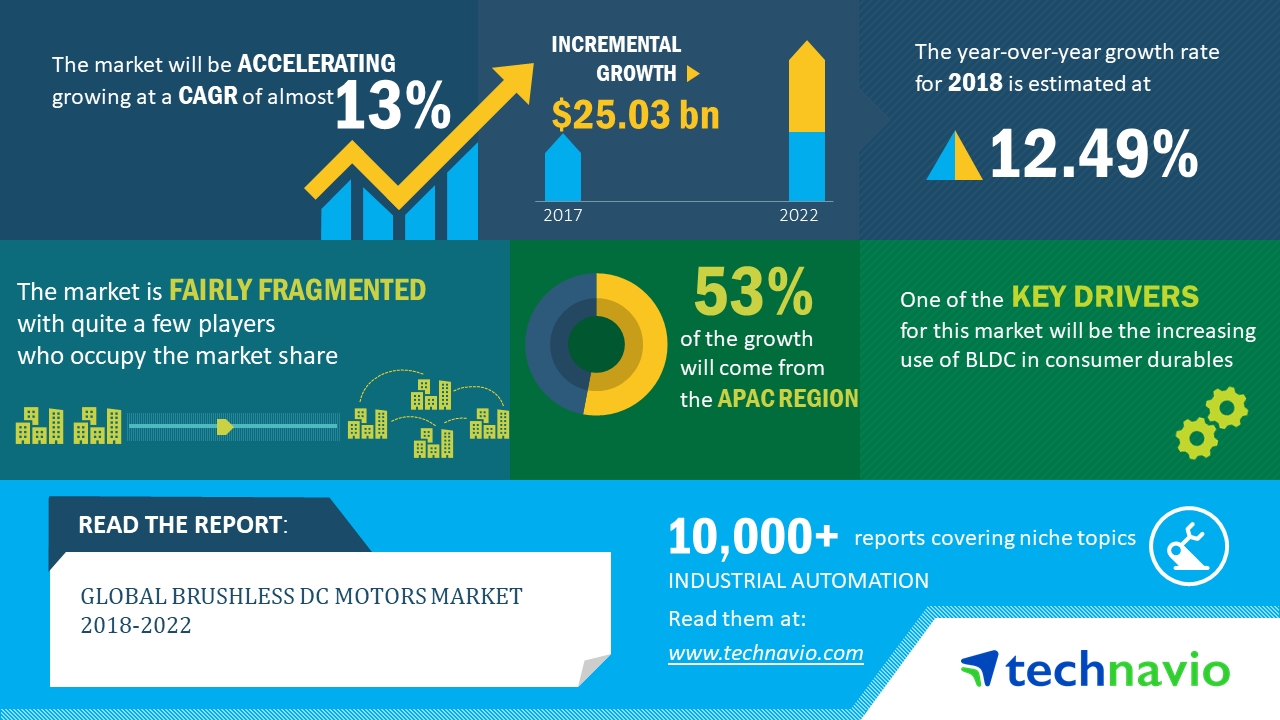
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Topics >> by >> the_definitive_guide_to_heav |
| the_definitive_guide_to_heav Photos Topic maintained by (see all topics) |
||
 Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor - onsemi for BeginnersAs the rotor rotates, the commutator chooses different windings and the directional current is applied to an offered winding such that the rotor's magnetic field remains misaligned with the stator and develops a torque in one instructions. Downsides of commutator [modify] The commutator has drawbacks that has actually resulted in a decline in use of brushed motors.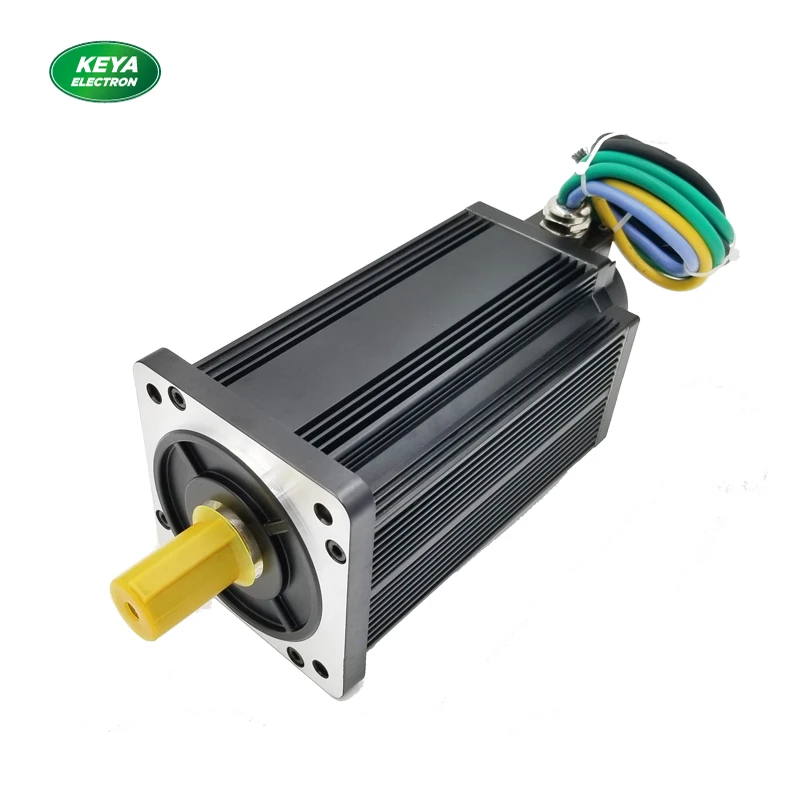  The soft brush material uses down due to friction, developing dust, and ultimately the brushes must be replaced. This makes commutated motors unsuitable for low particle or sealed applications like difficult disk motors, and for applications that need maintenance-free operation. The electrical resistance of the sliding brush contact causes a voltage drop in the motor circuit called brush drop which takes in energy. 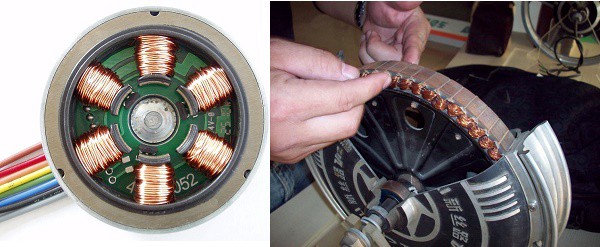 Throughout the last a century, high-power DC brushed motors, once the essential of industry, were replaced by alternating current (A/C) concurrent motors. Today, brushed motors are just utilized in low power applications or where just DC is available, however the above drawbacks limit their usage even in these applications. Brushless solution [modify] In brushless DC motors, an electronic servo system replaces the mechanical commutator contacts.  Brushed Versus Brushless DC Motors - Medical Design Briefs - QuestionsThe removal of the sliding contact allows brushless motors to have less friction and longer life; their working life is just restricted by the lifetime of their bearings. Brushed DC motors develop a maximum torque when stationary, linearly decreasing as speed increases. Some constraints of brushed motors can be conquered by brushless motors; they consist of greater effectiveness and lower vulnerability to mechanical wear. A typical brushless motor has permanent magnets that rotate around a repaired armature, eliminating problems related to linking present to the moving armature. An electronic controller changes the commutator assembly of the brushed DC motor, which continuously changes the stage to the windings to keep the motor turning. The controller performs similar timed power distribution by utilizing a solid-state circuit instead of the commutator system. With no windings on the rotor, they are not subjected to centrifugal forces, and due to the fact that the windings are supported by the housing, they can be cooled by conduction, requiring no airflow inside the motor for cooling. This in turn suggests that the motor's internals can be entirely enclosed and safeguarded from dirt or other foreign matter. |
||
|
||