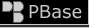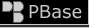Vultee BT-13B Valiant in World War II Gallery (8102-c) |

EARLY YEARS: 1909 Wright Military Flyer, 1st military heavier-than-air flying machine, U.S. Army Signal Corps (7928) |

Standard J-1, left, Bleriot Monoplane and Montgolfier balloon replica (DSCN7926) |

Standard J-1, right. Bleriot Monoplane, left, used for training & reconnaissance, 1st to fly across English Channel, 1909 (7930) |

Standard J-1 two-seat primary trainer: Used by the U.S. Army Air Service during World War I (7931) |

Standard J-1: Four companies -- Standard, Dayton-Wright, Fisher Body and Wright-Martin -- built 1,601 J-1s during WW I. (7977) |

SPAD VII, World War I, used by French Lafayette Escadrille, U.S. Army Air Service, and American Expedionary Forces (7934) |

French-built SPAD VII made its 1st flight in July 1916. It showed such promise that it was put into production at once. (7938) |

A few months after its 1st flight, the French-built SPAD VII appeared on the Front in both French and British squadrons. (7940) |

British-built Avro 504K -- Used by American Expeditionary Forces and U.S. Army Air Service during World War I (7937) |

Thomas-Morse S4C Scout was a single-seat training plane nicknamed "Tommy." It was used by U.S. pilots during World War I. (7964) |

Thomas-Morse S4C Scout U.S. training plane, left, and Fokker Dr. I triplane, German fighter, World War I (7942) |

Fokker Dr. I triplane: One was used by World War I's top ace, Germany's Rittmeister Manfred von Richthofen, the Red Baron (7943) |

Fokker Dr. I triplane reproduction: Among his scores, Manfred von Richthofen shot down 19 Allied planes with a Dr. I. (7962) |

French-built Nieuport 28, World War I, used by U.S. Army Air Service and American Expeditionary Forces (7951) |

British Sopwith F.1 Camel, re-creation, World War I, shot down more enemy planes than any Allied plane, used by U.S. (7955) |

Halberstadt CL IV supported German troops by attacking Allied ground positions with machine guns, grenades, small bombs. (7960) |

Curtiss JN-4D "Jenny," used for primary flight training during World War I and became mainstay of "barnstormers" in 1920s (7966) |

French-built SPAD XIII C.1, primary World War I fighter of U.S. Army Air Service, in ace Edward V. Rickenbacker's livery (7970) |

Kettering Aerial Torpedo "Bug," reproduction, World War I, unmanned, never saw combat, U.S. Army Air Service (7974) |

DeHavilland DH-4, used by U.S. Army Air Service as day bomber in World War I. U.S.-built, based on British design (7975) |

Fokker D.VII reproduction: World War I German fighter so superior over Allied aircraft, it downed 556 of them in Aug 1918 (7979) |

Standard J-1, World War I, used for primary flight instruction by U.S. Army Air Service, fabric covering fuselage removed (7983) |

Caproni CA.36 bomber: During WWI, Italian aeronautical engineer Gianni Caproni developed a series of heavy bombers. (7985) |

Caproni CA.36 bomber: Caproni's heavy bombers played a key role in the Allied strategic bombing campaign. (7988) |

Caproni CA.36 bomber: Caproni's bombers were produced not only in Italy, but also in France, Britain & the United States. (7991) |

Caproni CA.36 bomber: Toward the end of WWI, the definitive version, the Ca. 36, went into production. (7997) |

During World War I, the Allies used thousands of Ford Model T cars & trucks because of their low cost and ease of repair. (8010) |

Ford Model T: The ambulance version's light weight made it well-suited for use on combat areas' muddy & shell-torn roads. (8012) |

Packard LePere LUSAC 11 was the result of efforts to get an American-built fighter into combat as soon as possible. (7992) |

Packard LePere LUSAC 11: World War I ended before it saw combat, but U.S. Army Air Service used it during Interwar Years. (7993) |

Martin MB-2 (NBS-1), 1st U.S.-designed bomber, produced in large numbers during Interwar Years (8001) |

Martin MB-2 (NBS-1) replaced the British Handley-Page O-400 and Italian Caproni bombers produced in the U.S. during WWI. (8000) |

Consolidated PT-1 Trusty, 1st trainer bought in large quantities by U.S. Army Air Service after WWI, Interwar Years (8004) |

Eberhart SE-5E -- U.S.-made version used by U.S. Army Air Service after WWI for advanced training. (8061) |

Caquot Type R Observation Balloon used by U.S. Army in World War I & by British in World War II. Made in UK 1944. (8015) |

Left, Boeing P-12E fighter used by the Army and Navy (as F4B) between WWI and WWII. Right, Army's Curtiss P-6E "Hawk" (8017) |

Kellett K-2/K-3 Autogiro, cross between plane & helicopter. This K-2 was 1st autogiro tested by Army Air Corps, in 1931. (8018) |

Boeing P-26A "Peashooter," 1st all-metal monoplane produced for U.S. Army Air Corps, in 1930s (8020) |

Douglas O-38F reconnaissance plane of U.S. Army Air Corps in 1930s (8026) |

Martin B-10 was 1st "modern-day" all-metal bomber produced in quantity. It was used by U.S. Army Air Corps in the 1930s. (8028) |

Martin B-10: The aircraft on display, an export version sold to Argentina in 1938, is the only remaining B-10. (8031) |

Northrop A-17A, among the last of the prewar single-engine attack aircraft ordered into production by the Army Air Corps (8035) |

The North American NA-58, Army Air Corps designation BT-14, was a basic WWII trainer. Exhibit shows a training mishap. (8040) |

WORLD WAR II: The North American O-47B towed targets or flew coastal and antisubmarine patrols during World War II. (8045) |

North American O-47B: With the wings restricting downward vews and photography, windows were placed in the plane's belly. (8049) |

Curtiss O-52 Owls were used for observation & courier duties and submarine patrols off the U.S. coasts during WWII. (8036) |

De Havilland DH 82A Tiger Moth -- used during World War II to train most Royal Air Force pilots, including some Americans (8048) |

Hawker Hurricane MkIIa: Developed by the British in 1930s, the Hurricane won fame for its role in the Battle of Britain. (8059) |

Taylorcraft L-2M "Grasshopper" was not used in combat or sent overseas during WWII. It was used only for pilot training. (8070) |

Seversky P-35A, used by the U.S. Army Air Corps and Sweden in 1930s. Japan ordered 20 and used them during WWII. (8073) |

The P-35 was USAAC's first production single-seat, all-metal pursuit plane w/ retractable landing gear & enclosed cockpit (8074) |

Curtiss P-36A "Hawk," a forerunner of P-40, was used by U.S. Army Air Corps in late 1930s and early 1940s. (8064) |

Curtiss P-36A "Hawk": Soon after WWII began, the outmoded P-36 was relegated to training & courier duties within the U.S. (8065) |

Curtiss P-40E "Warhawk": The P-40 was the United States' best fighter available in large numbers when World War II began. (8075) |

Curtiss P-40E "Warhawk": P-40s engaged Japanese aircraft at Pearl Harbor and in the Philippines in December 1941. (8078) |

Douglas B-18 Bolo was the U.S. Army Air Corps' primary bomber from the late 1930s until 1941. (8080) |

Douglas B-18 Bolo served as the U.S. Army Air Corps' primary bomber until Boeing's B-17 came into WWII service in 1942. (8081) |

Mitsubishi A62M Zero: The Allies' main opponent in the Pacific air war, the Zero is a WWII symbol of Japanese air power. (8083) |

Mitsubishi A62M Zero: The fighter first flew in April 1939, and the Japanese navy produced 10,815 Zeros from 1940-1945. (8086) |

Mitsubishi A62M Zero: Kamikazes used Zeroes more than any other aircraft for their suicide missions. (8087) |

Mitsubishi A62M Zero: The Zero got its name from its official designation, Navy Type Zero Carrier-Based Fighter (Reisen). (8091) |

World War II diorama (8093) |

North American B-25B Mitchell: B-25 bombers were used by Gen. Jimmy Doolittle in the Tokyo Raid on April 18, 1942. (8096) |

North American B-25B Mitchell: The B-25 medium bomber was one of America's most significant World War II airplanes. (8097) |

Vultee L-1A Vigilant: The versatile WWII L-1 liaison plane towed gliders, transported supplies, performed rescues, etc. (N8098) |

Ryan PT-22 Recruit: Before 1939, the Air Corps relied on biplanes as primary trainers. In 1940 it started using Ryans. (8099) |

Douglas A-24 -- The U.S. Army Air Corps's version of the Navy's Dauntless dive bomber has a colorful history. (8103) |

Poorly regarded by combat pilots, Douglas A-24s served as training planes or towed targets for aerial gunnery practise. (8109) |

Beech AT-10 Wichita -- an advanced, multi-engine trainer that was designed to be easily manufactured in large numbers. (8113) |

Vultee BT-13B Valiant, basic trainer most widely used by USAAF during WWII. Basic: 2nd of 3 training stages. (8102) |

In 1943 all women pilots flying for the USAAF were consolidated into the Women Airforce Service Pilots (WASP) program. (8114) |

Women pilots served in flight training, gunnery target towing, engineering test flying, ferrying aircraft, other duties. (8115) |

Bell P-39Q Airacobra: The P-39 was one of America's first-line pursuit planes in Dec. 1941. 9,584 were made during WWII. (8116) |

Bell P-63E Kingcobra was developed from P-39 Airacobra and used for WWII training. Many were sent to the Soviet Union. (8117) |

Beech AT-11 Kansan was used as the standard World War II trainer for 90 percent of U.S. Army Air Forces bombardiers. (8120) |

Curtiss AT-9 Jeep/Fledgling was used as an advanced trainer to bridge gap between single-engine and twin-engine aircraft. (8122) |

"Tuskegee Airmen" served with distinction in combat and contributed to the eventual integration of the U.S. armed forces. (8126) |

Stearman PT-13D Kaydet: The U.S. and Allied nations used the Kaydet as a primary trainer from 1930s to the end of WWII. (8131) |

Bristol Beaufighter: This British plane filled the need for a night fighter in the U.S. Army Air Forces until 1945. (8134) |

Supermarine Spitfire Mk.Vc: The Spitfire won fame and admiration for its key role in the Battle of Britain in 1940. (8135) |

Supermarine Spitfire Mk.Vc: During the Battle of Britain, the Spitfire successfully fought the best German fighters. (8137) |

Supermarine Spitfire Mk.Vc: The Spitfire was produced in greater numbers than any other British aircraft during WWII. (8138) |

Supermarine Spitfire Mk.Vc: Though having many variants, the Spitfire was originally designed as an interceptor. (8142) |

Macchi MC.200 Saetta: Developed in the mid-1930s, the Saetta was one of the Italian Royal Air Force's main WWII fighters. (8149) |

Macchi MC.200 Saetta: By Italy's entry into WWII in June 1940, 156 were in service. A total of 1,151 were produced. (8151) |

Consolidated B-24D Liberator: The B-24 was employed in operations in every combat theater during World War II. (8144) |

Consolidated B-24D Liberator: Because of its great range, it was particularly suited for long-distance bombing missions. (8154) |

Consolidated B-24D Liberator: Its great range also made it suitable for long over-water missions in the Pacific Theater. (8162) |

Consolidated B-24D Liberator: More than 18,000 Liberators were produced. (8164) |

North American A-36A Apache dive bomber: first US Army Air Forces version of the Mustang, developed for the British. (8155) |

De Havilland DH 98 Mosquito was a British plane used by U.S. Army Air Forces for photographic and weather reconnaissance. (8158) |

Lockheed P-38L Lightning performed various missions during World War II, including bombing, strafing, long-range escort. (8167) |

Lockheed P-38L Lightning: The P-38 became the standard USAAF fighter in the Pacific until the closing months of WWII. (8169) |

Supermarine Spitfire Mk XI was was essentially a Mark IX interceptor modified for Allied photographic reconnaissance. (8171) |

Republic P-47D Thunderbolt was renowned for its ruggedness, firepower and speed. (8175) |

The massive Republic P-47 Thunderbolt was one of the most famous and important USAAF fighters during World War II. (8177) |

Republic P-47D "Razorback" Thunderbolt on display is an early version, nicknamed for the ridge behind the cockpit. (8228) |

P-47D "Razorback" is painted like the one Col. Neel Kearby flew. He named all his planes "Fiery Ginger," after his wife. (8231) |

Martin B-26G Marauder: The B-26 had the lowest loss rate of any Allied bomber -- less than one-half of one percent. (8181) |

Douglas C-47D: Few aircraft are as well known, were so widely used or used as long as the C-47. (8183) |

Boeing B-17G Flying Fortress: The B-17 is best known for the daylight strategic bombing of German industrial targets. (8193) |

Boeing B-17G Flying Fortress: The B-17 served in every WWII combat zone. From the 1930s until 1945, 12,726 were produced. (8195) |

Messerschmitt Bf 109G-10: During WWII, the Bf 109 was the backbone of the Luftwaffe fighter force. Over 30,000 were made. (8197) |

Junkers Ju 88D: This German plane was one of the most versatile WWII aircraft. It played many combat roles. (8201) |

Junkers Ju 88D: The aircraft on display is a long-range photographic reconnaissance version. (8204) |

Noorduyn UC-64A Norseman: 762 units of this Canadian plane was used by U.S. Army Air Forces as a WWII light transport. (8206) |

North American P-51D Mustang: The Mustang is among the best known and most admired U.S. fighters of World War II. (8209) |

North American P-51D Mustang: The P-51 operated primarily as a long-range escort fighter and ground attack fighter-bomber (8212) |

Focke-Wulf Fw 190D-9: One of Germany's best WWII fighter planes, it proved to be superior to Britain's Mark V Spitfire. (8215) |

Messerschmitt Me 163B: The rocket-powered Me 163's impact as a German WWII fighter was limited by technical problems. (8217) |

Messerschmitt Me 163B Komet: High fuel consumption severely limited its range. And its fuel was extremely hazardous. (8221) |

Messerschmitt Me 262A Schwalbe: This German WWII plane was the world's first operational turbojet aircraft. (8222) |

Messerschmitt Me 262A: This jet proved much faster than other WWII planes, but Allied bombings destroyed many of them. (8227) |

Douglas A-20G Havoc: Flown by the Allies in practically all theaters, the versatile A-20 went through many variants. (8234) |

The A-20G lived up to its name by bringing havoc and destruction in strafing attacks on Japanese shipping and airfields. (8276) |

Sikorsky R-4B: The R-4 was the world's first production helicopter, and the U.S. Army Air Forces' 1st service helicopter. (8235) |

Curtiss C-46D Commando: During WWII, the USAAF used 3,144 C-46s for hauling cargo and troops, and for towing gliders. (8238) |

Curtiss C-46D Commando: The C-46 gained fame during WWII transporting war materials over the "Hump" from India to China. (8243) |

Consolidated OA-10 Catalina: U.S. Army Air Forces' version of the PBY series used extensively by the Navy during WWII. (8253) |

Consolidated OA-10 Catalina is a monoplane with a flying-boat hull, retractable landing gear and retractable floats. (8254) |

Consolidated OA-10 Catalina: The OA-10 was used primarily for air-sea rescue during World War II and in later years. (8278) |

Northrop P-61C Black Widow: The heavily-armed P-61 was the first U.S. aircraft specifically designed as a night fighter. (8257) |

Northrop P-61C Black Widow: This WWII night fighter was used by the USAAF in Europe and the Pacific in 1944 and 1945. (8258) |

Kawanishi N1K2-Ja Shiden Kai (George) --- the best fighter used in significant numbers by the Japanese Navy during WWII. (8267) |

Kawanishi N1K2-Ja Shiden Kai (George): This maneuverable fighter was a formidable opponent in the closing months of WWII. (8272) |

Boeing B-29 Superfortress "Bockscar": "The Bockscar dropped the Fat Man atomic bomb on Nagasaki on Aug. 9, 1945." (8245) |

Boeing B-29 Superfortress "Bockscar": Meant as a replacement for the B-17 & B-24, the B-29 made its 1st flight in 1942. (8251) |

Boeing B-29 Superfortress "Bockscar": In 1943, the USAAF sent its B-29s to Asia, where they flew from China to Japan. (8249) |

Boeing B-29 "Bockscar": This B-29 has only one turret and no armor to save weight and fly farther with an atomic bomb. (8265) |

Boeing B-29 "Bockscar" with "demilitarized" versions of the Hiroshima "Little Boy" and Nagasaki "Fat Man" atomic bombs. (8259) |

The uniforms of enlisted Air Force personnel evolved over the years. (7925) |

National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson Air Base, Dayton, Ohio (8280) |